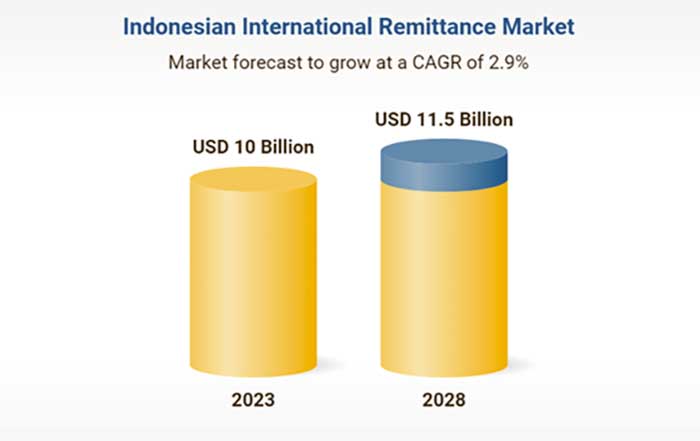
The fintech sector in Turkey has blossomed into a significant hub of innovation, boasting a diverse ecosystem of over 1000 fintech companies in 2024. This growth has been fueled by a combination of supportive regulatory frameworks, a resilient banking system, and a rapidly expanding digital infrastructure, making Turkey a promising ground for fintech ventures.
Regulatory Support plays a pivotal role in Turkey's fintech landscape, with proactive initiatives from the Central Bank of Turkey (CBT) promoting digital banking, electronic payments, and mobile banking. These initiatives have not only facilitated substantial investments in fintech startups but have also ensured a conducive environment for innovation to thrive. The regulatory environment is designed to balance openness to new ideas with safeguards to protect consumers, thereby fostering confidence and growth within the sector.
The Banking System in Turkey is renowned for its stability and adherence to stringent regulations, providing a robust foundation upon which fintech companies can build and expand their operations. The synergy between traditional banking institutions and fintech startups has been instrumental in driving sectoral growth, with banks increasingly viewing fintechs as partners in innovation rather than competitors. This collaboration has accelerated the pace of innovation, particularly in areas such as digital payments, financial inclusion, and customer-centric banking solutions.
Digital Adoption in Turkey has surged significantly, with over 65 million internet users and 70% smartphone penetration. This widespread digital infrastructure has created a fertile ground for fintech startups to introduce innovative financial products and services. The ease of access to digital platforms has enabled fintech firms to reach a broad audience, offering solutions ranging from mobile payment systems to digital wallets, thereby enhancing financial inclusion and accessibility across the population.
Fintech Startups in Turkey encompass a diverse array of offerings, catering to various financial needs and preferences. Companies like Paycell have revolutionized mobile payments and digital wallets, while iyzico has carved a niche in integrated payment solutions for e-commerce and business sectors. Additionally, TransferWise has facilitated cost-effective international money transfers, exemplifying the breadth of innovation within the Turkish fintech ecosystem.
Significant Investment Growth
The fintech sector in Turkey witnessed a significant increase in investments.
1000+ Fintech Companies
Turkey's fintech ecosystem boasts over 1000 companies.
65M+ Internet Users
Over 65 million internet users in Turkey, creating a fertile ground for fintech.
70% Smartphone Penetration
High smartphone adoption rate fuels digital financial services.
Global Fintech Hub
Turkey is poised to emerge as a significant player in the global fintech landscape.
Investment and Funding have played a crucial role in fueling the growth of fintech startups in Turkey. The sector witnessed a significant increase in investments in 2020, reflecting growing confidence from domestic investors in the potential of fintech ventures. This influx of capital has empowered startups to scale their operations, enhance service offerings, and expand their market reach both domestically and internationally.
Government Support remains pivotal, with Turkey's government offering various incentives to foster fintech innovation. Initiatives such as tax exemptions, reduced interest rates, and subsidies for research and development activities incentivize entrepreneurship and technological advancement within the sector. Moreover, the startup visa program encourages international entrepreneurs to establish their fintech ventures in Turkey, further bolstering the country's position as a global fintech hub.
Financial Inclusion is a key focus area for Turkey's fintech sector, aiming to extend access to financial services to underserved segments of the population. Fintech innovations such as mobile payment solutions and digital wallets have democratized access to banking services, empowering individuals who were previously excluded from traditional banking channels. This inclusivity not only fosters economic growth but also enhances social welfare by promoting financial literacy and empowerment.
Looking Ahead, the outlook for Turkey's fintech sector remains promising. The convergence of a supportive regulatory environment, a resilient banking system, and a digitally savvy population sets the stage for continued growth and innovation. As fintech startups continue to pioneer new technologies and expand their market presence, Turkey is poised to emerge as a significant player in the global fintech landscape. The ongoing evolution of financial services through innovation underscores Turkey's potential to shape the future of fintech on a global scale.
In conclusion, Turkey's fintech sector stands as a beacon of entrepreneurship and innovation, driven by its conducive regulatory framework, robust banking infrastructure, and expanding digital ecosystem. As the sector continues to evolve, fueled by investment, collaboration, and technological advancements, Turkey is well-positioned to lead the charge in redefining financial services for the digital age. The journey ahead promises continued growth, transformation, and impact, solidifying Turkey's place among the forefront of global fintech innovation.